| Line 61: | Line 61: | ||
Users can now get data from Elastic search for a given instance’s ''SysId'' so that they can look up the value and identify whether it is the latest or if a sync is needed. If the key exists, the latest value from ES will be displayed. If the key does not exist, the system will display the error message “Could not fetch value for provided SysId”. | Users can now get data from Elastic search for a given instance’s ''SysId'' so that they can look up the value and identify whether it is the latest or if a sync is needed. If the key exists, the latest value from ES will be displayed. If the key does not exist, the system will display the error message “Could not fetch value for provided SysId”. | ||
<div class="note-box">'''Note''': Data can be fetched from only one instance at a time.</div> <div class="image-green-border">[[File:Search Sync ES.png|720px|Search Sync ES.png]]</div> <div class="image-green-border"> </div> | <div class="note-box">'''Note''': Data can be fetched from only one instance at a time.</div> <div class="image-green-border">[[File:Search Sync ES.png|720px|Search Sync ES.png]]</div> <div class="image-green-border"> </div> | ||
| + | |||
== Translations Editor Tool == | == Translations Editor Tool == | ||
| Line 90: | Line 91: | ||
2. For bulk editing and updation of multiple languages and resource keys, use the Download / Upload option to download an MS Excel sheet. | 2. For bulk editing and updation of multiple languages and resource keys, use the Download / Upload option to download an MS Excel sheet. | ||
| − | '''<span style="color:#008000;">Selective Editing to Update Translations</span>''' | + | |
| − | + | <div class="image-caption">'''''<span style="color:#008000;">Selective Editing to Update Translations</span>'''''</div> | |
For editing Resource Key values selectively: | For editing Resource Key values selectively: | ||
| Line 111: | Line 112: | ||
<div class="image-green-border">[[File:Translation Editor 6.png|720px|Translation Editor 6]]</div> | <div class="image-green-border">[[File:Translation Editor 6.png|720px|Translation Editor 6]]</div> | ||
You can select the respective languages (French or Spanish) to verify that the resources have been successfully updated. | You can select the respective languages (French or Spanish) to verify that the resources have been successfully updated. | ||
| − | <div class="image-green-border">[[File:Translation Editor 7.png|720px|Translation Editor 7]]</div> <div class="image-caption"> </div> <div class="image-caption"> </div> <div class="image-caption"><span style="color:#008000;">Bulk Editing in Multiple Languages</span></div> | + | <div class="image-green-border">[[File:Translation Editor 7.png|720px|Translation Editor 7]]</div> <div class="image-caption"> </div> <div class="image-caption"> </div> <div class="image-caption">'''<span style="color:#008000;">Bulk Editing in Multiple Languages</span>'''</div> |
For editing Resource Key values of multiple languages in bulk: | For editing Resource Key values of multiple languages in bulk: | ||
Revision as of 07:23, 4 August 2020
Contents
Self-Serve Tools
Self-Serve tools include tools and features of ICM that can be used out-of-the-box by authorized users. Besides serving ICM users with specific feature and performance goals, being self-sufficient is the primary goal of these tools. These tools are user-friendly and time-saving, enabling users to perform tasks by themselves instead of reaching out to Icertis Solutions Engineering, Database or Support teams based on the requirement. Sometimes, these changes were minor and of low complexity, but the turnaround time was substantial.
The ICM Self-Serve tools include:
- Search Sync Tool
- Translations Editor Tool
- Improved ICM Health Check Tool
- Configurations Key Editor Tool
- Promote to Production (P2P) Tool
- The ICM application, version 7.11 and above
- The user must have valid credentials to access ICM and the User Administration tile.
Search Sync Tool
The Search Sync tool gets data from Elastic Search (ES) for a given instance’s Sys Id and synchronizes it if required. Using the fetched ES value, the tool validates if the Sys Id is the latest for the respective instance or if a sync is required. This tool can be accessed by the Administrator from the Admin Task on User Administration tile.
If the key exists, the latest value from ES will be displayed. If the key does not exist, the system displays an error message indicating that the value could not be fetched for the provided Sys Id. The Sys Id can be provided as input CSV file or as comma separated. Either comma separated Sys Ids can be entered or a CSV file can be uploaded.
This helps to make the entity search more streamlined and efficient. Users can quickly refer to related agreements at the time of deals or audits.
Note: Data can be fetched from only one instance at a time. A dedicated key must exist for ES sync to work with Sys ID.
You can search the documents that an Agreement is linked to.
To use the Search Sync Tool:
1. Click Home > User Administration > Admin Task. The Admin Task page opens.
2. Click the Search Sync task from the left pane.
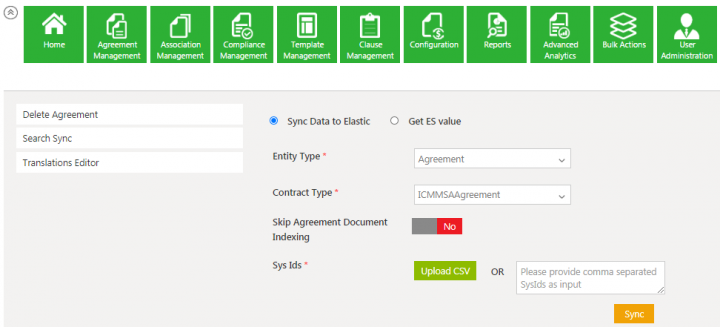
4. Select the Entity Type from the drop-down to sync data to the Elastic Search. For example, Agreement.
5. Select the Contract Type from the drop-down.
5. Toggle Skip Agreement Document Indexing to Yes/No as required.
6. To get the Sys Ids, click the Upload CSV button to upload the .CSV Agreement or enter the Sys Id using comma separated value in the box.
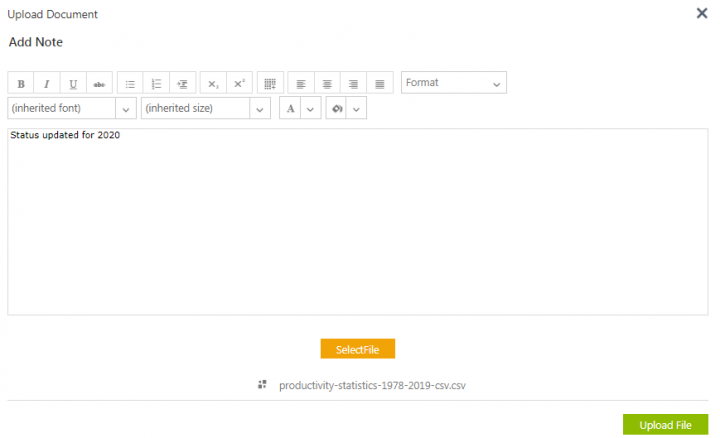
7. Click the Upload CSV button to upload the CSV document. The Upload Document window opens.
8. Click SelectFile to upload a CSV file and add a note if required.
9. Click Upload File. The file is uploaded to the File Path displayed.If the uploaded file format is incorrect, an alert message is displayed. The supported file formats will be also be displayed.
If the uploaded file format is incorrect, an alert message is displayed. The supported file formats will be also be displayed.
10. Click Sync. The Sync Request Accepted message is displayed.
11. Click Ok. Users can now get data from ES for a given instance’s SysId and can check if it has the latest value or if a sync is needed.
12. Select Get ES Value.
13. Enter the SysId and click Go. If the key exists, the latest value from ES will be displayed. If the key does not exist, the error message Please enter valid SysId is displayed.
Users can now get data from Elastic search for a given instance’s SysId so that they can look up the value and identify whether it is the latest or if a sync is needed. If the key exists, the latest value from ES will be displayed. If the key does not exist, the system will display the error message “Could not fetch value for provided SysId”.
Translations Editor Tool
The ICM platform is available in different languages and different languages label text are available for localization. However, to make any changes to the localization values, users had to reach out to the Solutions Engineering or Database teams. Sometimes, these changes were minor and of low complexity, but the turnaround time was substantial.
Hence, a self-service Translations Editor tool has been introduced that contains all strings that are localized.
Users can now download all keys and their localization values as an Excel file, modify multiple values, and upload the modified changes to ICM. Once the values are updated in ICM, the caches are updated automatically to avoid the cache flush and server restart. This has significantly enhanced productivity as the turnaround time to update the Resource Key values has been eradicated.
Using this tool, users can now:
- Search for a specific string using the search bar and update the Resource Key value for Language and Locale.
- Update multiple language strings by selecting and saving the Resource Key value.
- Download and upload the localization key values using Microsoft Excel.
- View the modified values in the ICM instance immediately.
To use the Translations Editor Tool:
1. Click the User Administration tile on the Home page.
2. Select Admin Task from the drop-down. The Admin Task page opens.
3. Select the Translation Editor task from the left pane.
Users can update translations in the following ways:
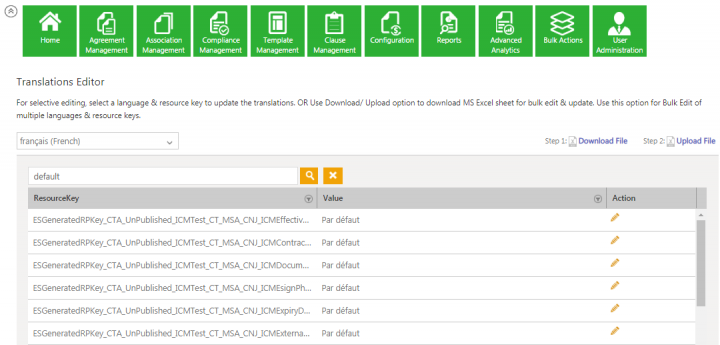
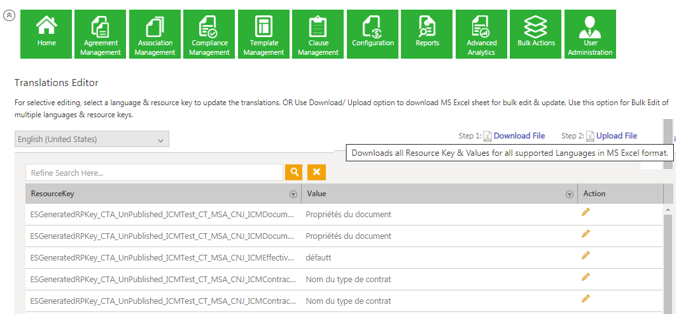
1. For selective editing, select a language and a resource key to update the translations.
2. For bulk editing and updation of multiple languages and resource keys, use the Download / Upload option to download an MS Excel sheet.
For editing Resource Key values selectively:
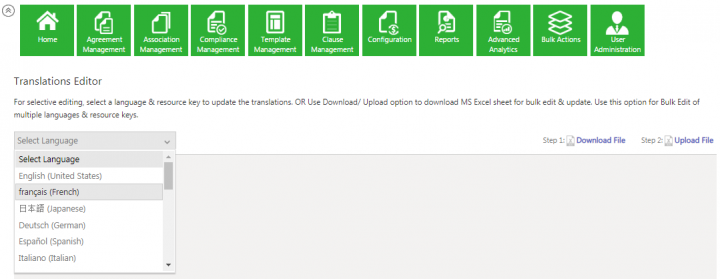
1. From the Select Language drop-down, select a language in which you want to edit the labels. For example, français (French).
The Resource Key and respective values of the selected language are displayed.
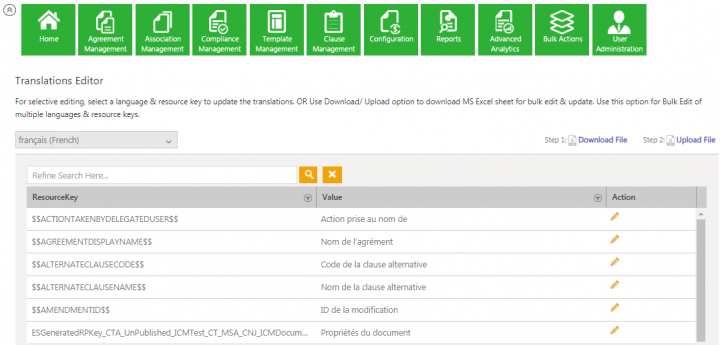
2. Enter a ResourceKey value in theSearch field to edit. For example, default. All ResourceKey(s) with the Par défaut (default) values from the French language are displayed.
Note: ResourceKey is a unique key by which the application gets its label text for different languages.
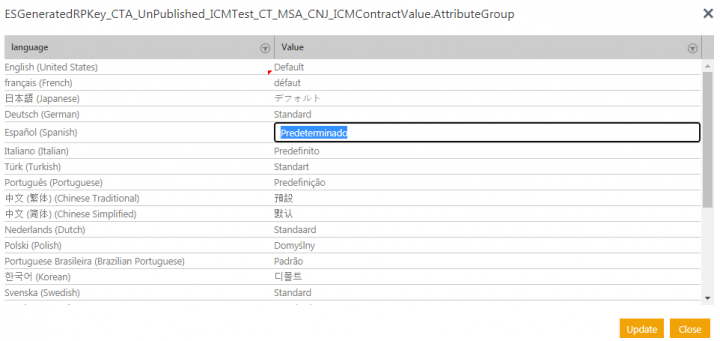
3. Click the Edit this Resource Key for Multiple Languages icon in the Actions column.
You can change the key for a single language or for multiple languages as required. For example, change Par défaut to défaut in French or Predeterminado in Español (Spanish) to Defecto.
4. Click Update. The ResourceKey value for default is updated to défaut for French and to Defecto in Spanish.
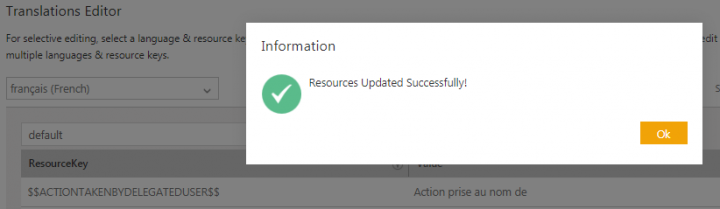
5. The Resources Updated Successfully message is displayed. Click Ok.
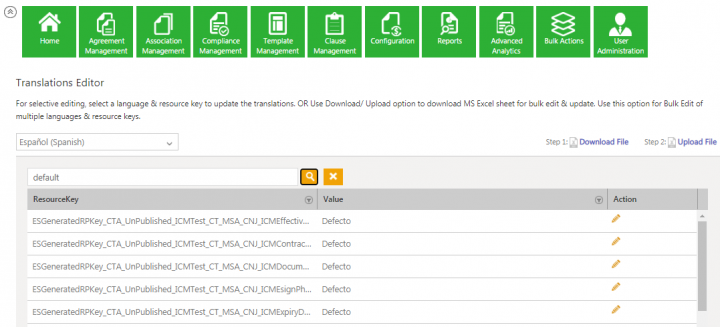
You can select the respective languages (French or Spanish) to verify that the resources have been successfully updated.
For editing Resource Key values of multiple languages in bulk:
1. Click Download File. A Microsoft Excel file (named BulkActionWorkBookStringResource) that contains all the Resource keys and values for all supported languages in ICM is downloaded.
2. Open the downloaded Microsoft Excel file.
3. Click Enable Editing. All ICM supported language Resource keys and their respective values are displayed.
4. Edit the ResouceKey of multiple languages as required.
5. Save the Excel file.
6. Click Upload File. The Upload Translations window opens.
7. Click SelectFile. The Open window opens.
8. Select the updated Excel file.
9. Click Open. A warning window opens indicating that this is a heavy operation and can potentially affect overall application performance.
10. Click Ok. The Upload Summary displays the number of Records Uploaded, Records Processed, andRecords Updated Successfully values.
11. Click Close. The label translations have been achieved for multiple languages in bulk.
ICM Health Check Tool
The ICM platform hosted on Azure Cloud uses services such as Elastic Search, Redis along with internal components such as APIs and Task services. However, no services were used to provide an insight on the application health except for the ICM Health Check page that provided regular application health checks and application monitoring to be able to detect issues before they became full-fledged outages.
The ICM Health Check page has been further extended to cover additional parameters to help identify potential outages and diagnose issues. The health insights will provide information on how well the ICM Instance and its service is performing, its overall health, as well as its usefulness to users. Users will now be able to access a dashboard (without logging into ICM) that tracks application health alongside usage metrics and application crash data.
The health statuses are classified into three categories:
- Warning - This is indicated with a yellow warning icon
- Healthy - This is indicated with a green check mark icon
- Unhealthy - This is indicated with a red warning icon
The following details are displayed in the Health Check:
- Elastic Search Health: This displays the Status (yellow/green/red), the Elastic Search version and the Uptime, and so on.
- Redis Cache Health: This displays the Redis version, Uptime In Days, CPU usage, Connections Received and Commands Processed, and so on.
- API Health: This displays the API Response Time, Status and Issues and so on.
- Database Server Metrics: This displays the CPU usage percentage, User Connections, Total Server Memory, Disk Read/Write IO/Sec and so on.
- IIS Server Metrics: This displays % 404 HTTP Response Sent, % 500 HTTP Response Sent, percentage of CPU utilization per process, Requests/sec, and so on.
To check the health of your system:
1. Enter /health/viewhealth at the end of the URL of your ICM instance. For example, https://apexorg.icertis.com/health/viewhealth. The various tools and their health are displayed.
2. Click the + icon next to the tool to view details regarding its health. The details for each of the tools are displayed in 2 columns with the Keys and their respective values as shown below.
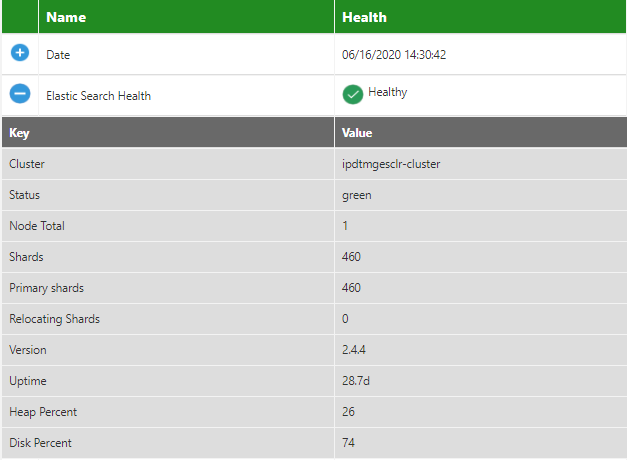
Elastic Search Health
The details for the Elastic Search Health include the status, node total, primary and relocating shards, version, heap percent, uptime, and so on. For example, the Status is green.
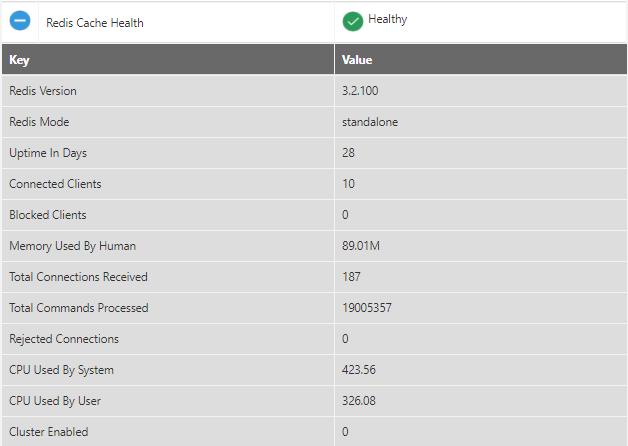
Redis Cache Health
The details for the Redis Cache Health include the uptime in days. Connected or blocked clients, rejected connections, CPU usage, and so on. For example, the Uptime in Days is 28.
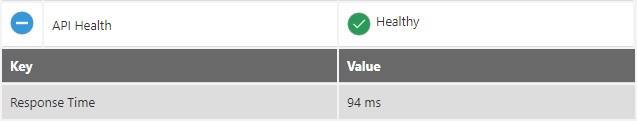
API Health
The API Health provides the response time. For example, 94 ms.
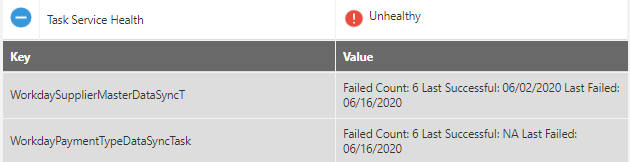
Task Service Health
The Task Service Health provides the failed count for keys and when it was last successful.
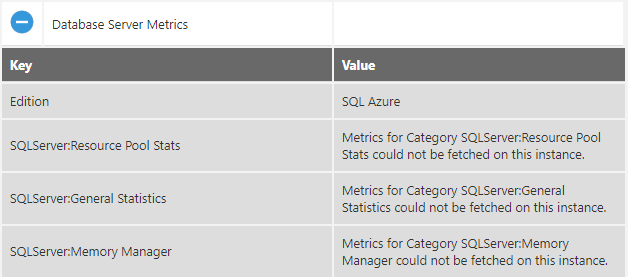
Database Server Metrics
The details for the Database Server Metrics Health include the edition, SQL server resource pool stats, and so on.
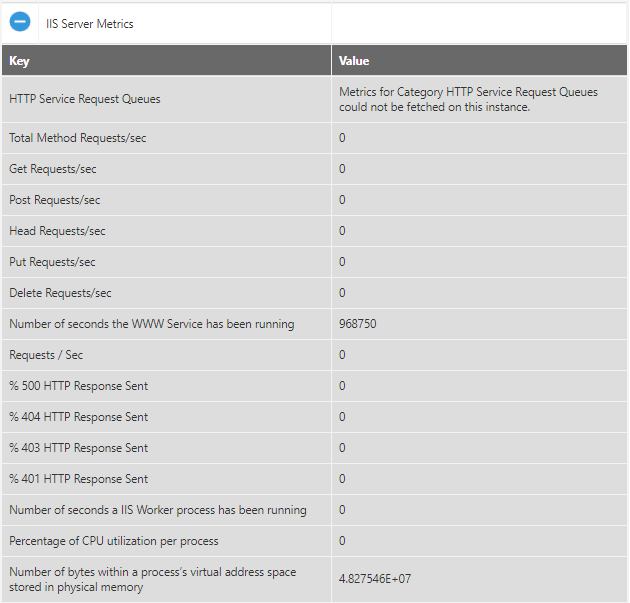
IIS Server Metrics
The details for the IIS Server Metrics Health include the total method requests/sec, number of seconds an IIS Worker process has been running, the percentage of CPU utilization per process, and so on.
Configuration Key Editor Tool
The Configuration Key Editor tool facilitates a logged-in user (who has access to Azure subscription) to search and update configuration keys, as and when required. It has been introduced for easier instance management and improved productivity, thus reducing the dependency on the Engineering and DevOps teams.
It includes:
- The Config Editor
- The Redis Flush
The Config Editor is a self-service tool that allows teams to edit instance configurations without having to connect to the instance machines. Once the key values are changed, the cache is automatically updated to avoid the server restart. The tool only works for non-production environments. The production environment configuration changes are controlled by Operations team, and the tool would not be available for production environment.
The Redis Flush is a self-service tool which allows Administrators to flush the cache or look up a particular key for its value of Delete a Key. The tool can also be used to perform Role Restart on the instances to which the user has access.
To use the Configuration Key Editor Tool:
1. Login to the ICM Tools portal (icmtools.icertis.com) with your ICM credentials.
3. Select the environment from the Environment CName drop-down that you need to access for configuration. All the instances that have you have access to will be displayed.
4. Click Submit after selecting the environment. The configuration json files for the selected environment are displayed for all available features, security details, database connections, and so on related to the selected instance.
5. Select a Config Key from the list to change its value as required. For example, the Config Key AgreementAutoRenewReminderNotificationPeriod has the reminder period set at 3 days may be changes to 2 days.
6. Click Save and Role Restart to save the new value of 2 days. The specific json file for the respective CName will be reset (i.e. perform a role restart). This means that the configuration is reset in the elastic search and the server is restarted, so that the new value is reflected on the instance.
7. Click Download to download the entire file so that you can edit it offline and then upload it directly to the instance.
Promote Configurations (P2P) Tool
The Promote to Production (P2P) process of the ICM platform helps to move ICM Configuration from source (Config/UAT) environment to target (production) environment. P2P process enables to selectively move ICM configuration. The Promote Configuration Tool or P2P is designed to accomplish just that.
With the 7.11 release, the Promote to Production (P2P) tool to enable users with the following enhancements:
- Vulnerability and Penetration Testing (VAPT) fixes
- Testing open bugs in P2P engine
- Some new validations in the P2P engine
- Better user interface to provide support to P2P and DevOps teams
With the 7.12 release, changes have been made in ICM to support the P2P engine. This functionality, provided to Administrators, can promote ICM configurations/modifications that are made to ICM configurations in pre-production environments to production environments. This tool provides support for contract types, contract type attributes, clauses and templates (along with the documents), notification templates, rules, masterdata, users, user groups and security groups. The elastic search sync is also supported by the tool.
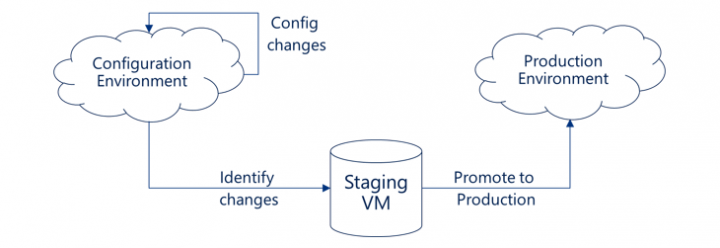
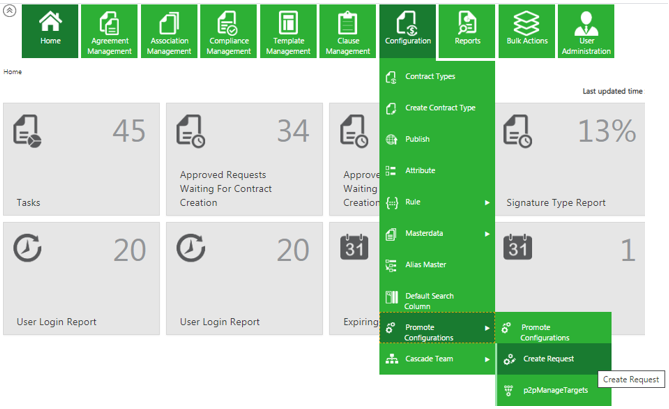
Here is an overview of the P2P process:
To access the P2P tool:
1. Click Home > 'Configurationtile. The Configuration page opens.
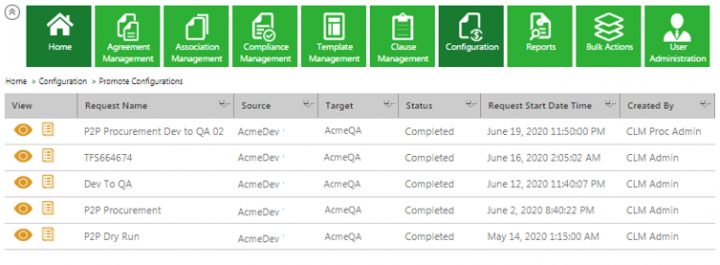
2. Click the Promote Configurations tile. The Promote Configuration page opens. The Promote Configurations displays the current status of PToP requests and their status.
Note: Users cannot edit a request that is in Completed state.
To create a P2P Request:
1. Click Configurations > Promote Configurations > Create Request. The Create P2P Request page opens.
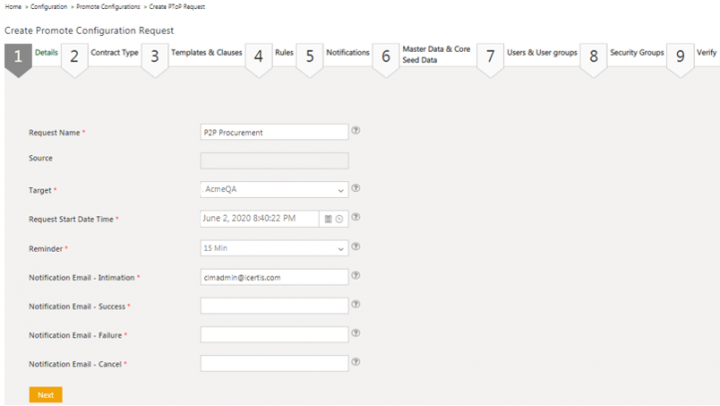
2. Enter a Request Name. For example, Procurement.
3. Select a Target from the drop-down. For example, Acme Dev.
4. Select the P2P Request Start Date Time.
5. Select the time to trigger an email to the recipient from the Intimation Email minutes before P2P Starts drop-down list. For example, 15 Min.
6. Enter the intimation recipient Email Id in the Notification Email – Intimation field.
7. Enter the notification recipient Email Id in the Notification Email – Success field.
8. Enter the notification recipient email Id in the Notification Email – Failure field.
9. Enter the notification recipient email Id in the Notification Email – Cancel field.
10. Click Next. The Contract Type tab opens.
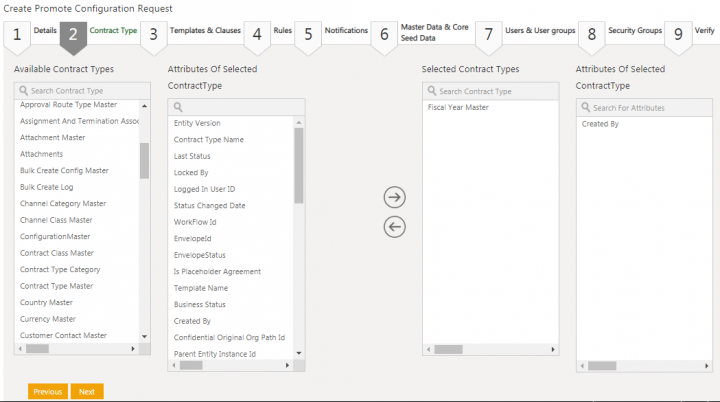
11. Select the Contract Type from the Available Contract Types. For example, Fiscal Year Master. The selected Contract Type attributes are available in the Attributes Of Selected Contract Type columns.
12. Select the attributes for the selected contract type. For example, Created By.
13. Click the right arrow to move the selected contract type and attribute to the Selected Contract Types and Attributes Of Selected Contract Type columns respectively.
14. Click Next. The Templates and Clauses tab opens.
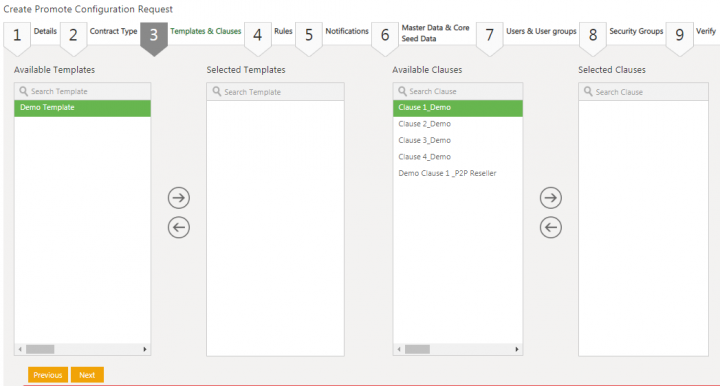
15. Select a template from the Available Templates columns. For example, Demo Template.
16. Click the arrow key to move the selected template to the Selected Templates column.
17. Select a clause from the Available Clauses columns. For example, Clause 1_Demo.
18. Click the arrow key to move the selected clause to the Selected Clauses column.
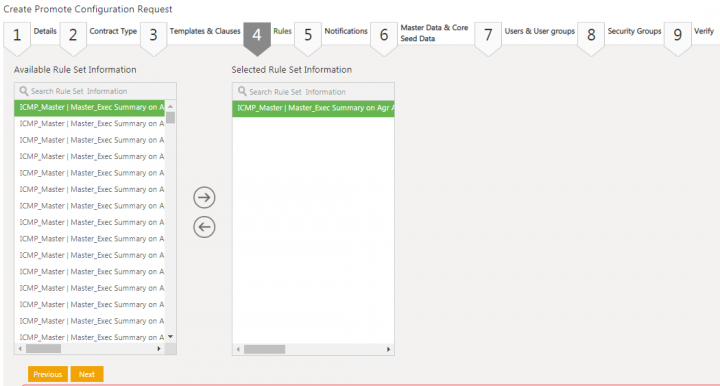
19. Click Next. The Rules tab opens.
20. Select a Rule from the Available Rule Set Information column. For example, ICM_Master I Master_Exec Summary on Agr Add Association.
21. Click the arrow key to move the selected rule to the Selected Rule Set Information column.
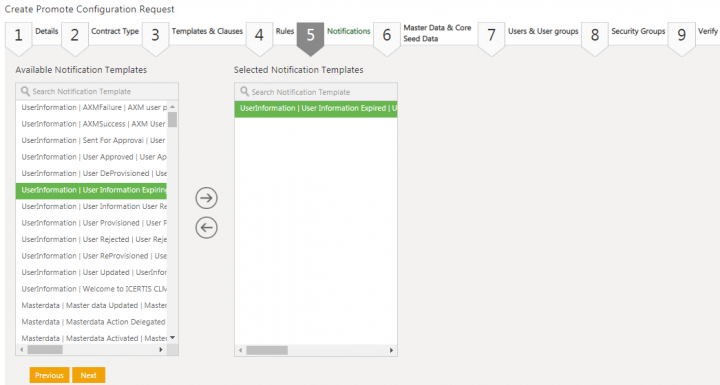
22. Click Next. The Notifications tab opens.
23. Select the notification template from the Available Notification Template columns. For example, UserInformation I User Information Expired I UserInformationExpired I User Notifications.
24. Click the arrow key to move the selected template to the Selected Notification Templates column.
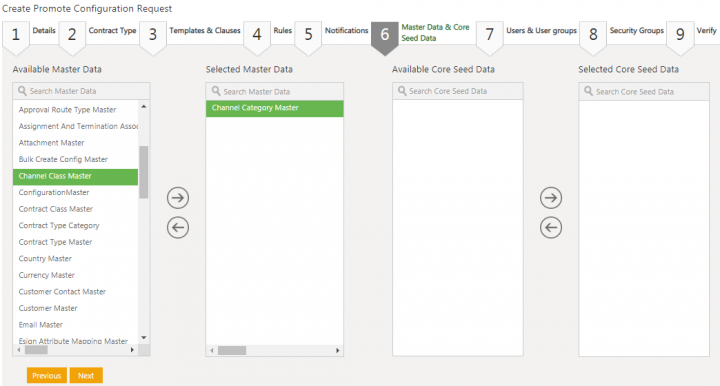
25. Click Next. The Master Data & Core Seed Data tab opens.
27. Click the arrow key to move the selected rule to the Selected Master Data column.
28. Select the seed data from the Available Core Seed Data column.
29. Click the arrow key to move the selected master data to the Selected Core Seed Data column.
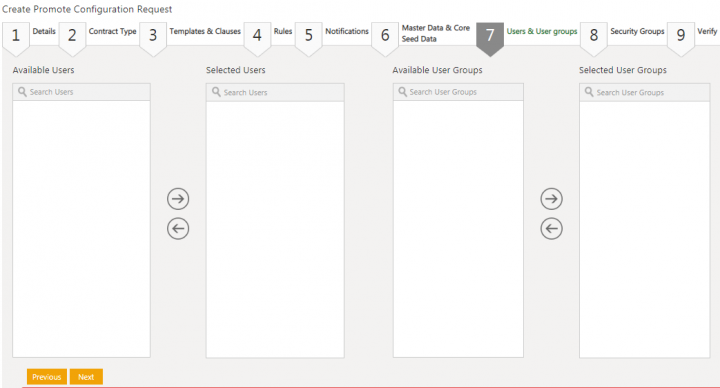
30. Click Next. The Users & User groups tab opens.
31. Select the users from the Available Users column.
32.Click the arrow key to move the selected user to the Selected Users column.
33. Select the user group from the Available User Groups column.
34. Click the arrow key to move the selected user to the Selected User Groups column.
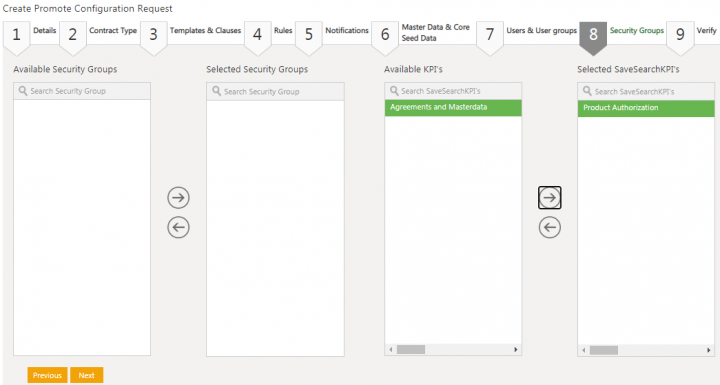
35. Click Next if any or no user or user group is selected. The Security Groups tab opens.
36. Select the security group from the Available Security Groups columns.
37. Click the arrow key to move the selected security group to the Selected Security Groups column.
38.Select the KPI from the Available KPI’s columns.
39.Click the arrow key to move the selected KPI to the Selected SaveSearchKPIs column. For example, Product Authorization.
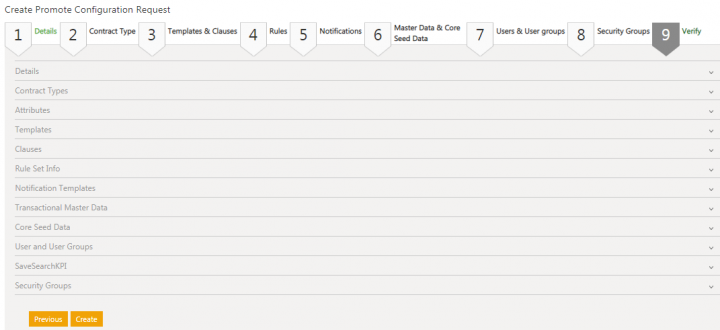
40. Click Next. The Verify tab opens.
41. Verify details of the contract types, attributes, templates, clauses, rule set information, notification templates, master data, core seed data, user and user groups, save search KPI and security groups that you have selected.
42. Click Create. The Please Confirm window opens indicating that downtime is required for this request.
43.Click Yes if you wish to proceed. The Information window opens indicating that the P2P request created successfully.
44.Click Ok. The P2P request status changes to ADDED.
45. On completion of the P2P request, the status changes to Completed.
Related Topics: Agreement Management | Association Management | Compliance Management | Template Management | Clause Management | Configuration | Reports | Localizing ICM